How ransomware is a big problem for small business – and what to do about it

Imagine trying to log into your business’s computer only to find that your files have been taken hostage. You must either pay up or lose your data forever.
It sounds like a scene from a TV drama, but small businesses across the country are increasingly under attack. According to a recent study, the average ransom demand was for $750,000 [PDF].
Ransomware is the software behind cyber extortion, an internet crime where your data or device is held for ransom. Cyber criminals attack small businesses because they usually have fewer security measures in place, making them easy and profitable targets. Remote work security risks further increase the danger, as employees accessing sensitive files from home or other offsite locations may inadvertently expose your systems.
As a small business owner, you can’t afford an attack. But before learning how to defend your business from ransomware, you need to understand what it is.
What exactly is ransomware?
Ransomware is typically activated when someone clicks a link in a social engineering or a phishing email or downloads an email attachment. Once activated, it can take over a computer or even an entire network.
Ransomware can also be delivered through security holes and infect a system without any action on the part of a user. Older, unsupported versions of Microsoft Windows are particularly vulnerable to ransomware and malware attacks, and even newer systems are vulnerable if they aren’t updated with patches for known security issues.
According to a recent data breach report from Verizon, ransomware is typically present in 70% of malware breaches. This is why it's important to understand where and how ransomware can affect you.

Types of ransomware
There are two main types of ransomware used in a malware attack:
- Locker ransomware locks the users out of their devices. This is the simplest form, and sometimes a cybersecurity expert can restore access.
- Crypto ransomware encrypts users’ data. If data is encrypted, it cannot be accessed without a unique decryption key the hackers may or may not have.
Once ransomware is planted, your computer will usually show a message from the hackers. It may demand payment to restore access to your files or unlock your computer. It might also threaten to publish sensitive data if you don’t pay up.
Ransom demands may ask for hundreds or thousands of dollars in payment in bitcoin or another cryptocurrency. They usually give a payment deadline of just a few days. If you don’t pay, your data will be destroyed or published.
What’s the difference between ransomware and DDoS attacks?
Ransomware and distributed denial-of-service attacks (DDoS) often go hand in hand. In a DDoS attack, a hacker sends a flood of internet traffic at the targeted system. This overwhelms the system to the point where it slows to a crawl or stops.
Hackers may threaten to bring your small business offline with a DDoS attack unless you pay a ransom. More commonly, hackers use DDoS attacks to temporarily bring down firewalls and other security infrastructure. This gives them time to install the ransomware.
Cyber criminals are targeting small businesses with denial-of-service and ransomware attacks with increasing frequency. And the costs of these attacks are also growing.
Why ransomware should alarm your small business
The trend of storing data in the cloud, accepting online payments, and doing most business online isn’t slowing down.
That’s why cyber crimes like ransomware are also on the rise.
For hackers, the internet is like handing a bank robber the combination to the vault. They can easily get past a business’s cyber defenses to wreak havoc and get rich in the process. And with so many businesses online, there are plenty of potential victims.
In the past, cyber criminals went after big targets like governments, hospitals, and universities. They knew these organizations could be paralyzed by an attack and could afford to pay a ransom.
But now, small businesses are the targets of 82% of ransomware attacks.
Why? Because you’re easy prey.
Small businesses often lack the security or training to prevent an attack. If you’re in finance, healthcare, or online retail, you’re more likely to be targeted. In fact, some of the biggest business sectors at risk for a cyber attack are:
- Media, entertainment, and leisure
- Business, professional, and legal services
- Construction and property
- IT, technology, and telecoms
- Financial services
But any small company that conducts business online, stores data, or simply uses computers to manage their business is at risk.
The costs of a ransomware attack
The potential costs of ransomware go well beyond the price of the ransom. Most businesses attacked experience significant downtime, resulting in lost revenue. Which could also lead to lost customers and potential new business.
Sometimes the cheapest solution is to pay a ransom. Yet doing so fuels a vicious cycle of cyber crime against small businesses. It also provides no guarantee your data will be restored. And losing valuable customer, vendor, or other information could cause long-term damage to your business.
Even outside the significant lost revenue, there are regulatory fines that must be paid, lawsuits, and notification and credit monitoring costs that can drag out for a year or more. Which all comes with a hefty price tag.
Additionally, with the continued uptick in ransomware attacks and data breaches, the cost of cyber liability insurance has risen as well. In 2022, U.S. cyber insurance premiums surged 50% as the demand for coverage increased.

How much does cyber insurance cost?

Insureon customers pay an average premium of $145 per month for cyber insurance. The cost of cyber liability insurance is based on several factors including:
- Amount of sensitive data handled
- Your industry
- Coverage limits
- Number of employees
All of these factors will be instrumental in determining how much cyber insurance your small business needs.

How you can prevent an attack
Ransomware is a sneaky threat. The good news is, it’s preventable.
Small businesses can protect against ransomware using several common-sense methods. It’s also worth investing in antivirus programs and other basic security measures.
Security measures you can take include:
- Scanning computers with antivirus software on a regular schedule.
- Configuring your firewall to prevent ransomware.
- Training your employees on best practices, such as opening only trusted attachments.
- Backing up your business data on a regular basis and storing it offline.
- Keeping your operating system’s security patches up to date.
- Filtering emails to prevent spam from reaching employees.
- Limiting the number of administrative privileges given to employees.
- Switching to two-factor authentication so a compromised password alone won’t give away your data.
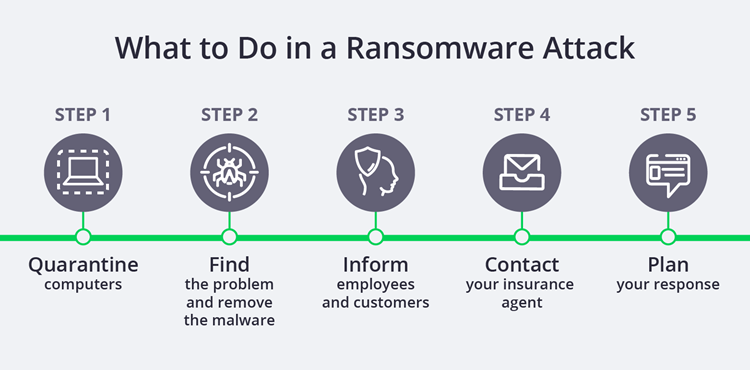
What to do if you are attacked
When you learn you’ve been attacked, take these steps to limit your damages and costs.
1. Quarantine the affected machine
To prevent ransomware from spreading, immediately isolate the infected computer or system. Turn off any potentially infected machines and disconnect them from the network.
Remember that the hackers may not have told you everything. Malware could be on multiple computers. Check everything and isolate any potential issues.
2. Remove the malware and identify the security weakness
Even if you decide to abandon the stolen data, you still need to deal with the infection and control its spread. Also make sure to notify your local law enforcement and the FBI.
After the malware is removed, change your passwords immediately. You’ll also want to diagnose what exactly led to the attack so you can prevent it from happening again.
3. Inform employees and customers
Break the news to your employees first. If system downtime will affect your customers, inform them too.
It’s important that you tell customers why they may experience customer service issues and when issues may be resolved.
4. Contact your insurance agent
If you have cyber insurance, call your insurance agent right away. They may be able to help you respond and may handle payment directly should you choose to pay.
Following a ransomware attack, your cyber liability policy can cover the costs of:
- Paying the ransom.
- Business interruption expenses such as the cost of hiring additional staff, renting equipment, or purchasing third-party services.
- Hiring an expert to find and repair the security flaw.
- Notifying your customers.
You may also want to find a consultant to help with your response and recovery.
5. Plan your response
Once you’ve shared the issue and rallied your troops, decide how you’ll respond. Your options include:
- Try to regain access. This might be possible if your system is attacked by locker ransomware. If your screen is locked, contact an expert to see if there’s a way to remove the ransomware and regain access.
- Restore the data. You could back up your system to the most recent version.
- Abandon the data. Even if you don’t have a backup, you may choose to simply forfeit the data if it wasn’t critical to business operations.
- Pay the ransom. It’s your choice. However, this option is not guaranteed to work.
6. Think twice before paying up
Your data may not be unlocked after payment. Plus, the hackers may demand even more money. Worst of all, it shows hackers that cyber extortion works, which means more businesses will suffer these attacks.
If you do decide to pay, first ask for “proof of life.” This is a demonstration that the hackers can actually decrypt your files. The hackers might show they can decrypt one file as proof they can restore your data.
Once you pay the ransom, the best-case scenario is that the hackers provide a decryption key that restores access to your data – but there’s no guarantee that will happen. In the WannaCry attack, few if any of the victims who paid recovered their data.
This loss of data is a big reason why the impact of a cyber crime can be felt long after an attack is over.
How to recover from a ransomware attack
Ransomware attacks can bankrupt a small business, even if the data is recovered. Downtime during the attack can result in lost profits, and your customers may decide to take their business elsewhere.
Beyond the damage to your customer base, your company likely paid for extensive technical support or an expensive ransom fee. Even if your data was backed up, it still costs time and money to get your business back online.
These steep costs and lasting damage are why cyber liability insurance is highly recommended. And if your small business operates online or works with sensitive data, you’re at even greater risk.
Consider cyber insurance to protect your business from future attacks
Cyber liability insurance helps your business during and after a ransomware attack. It can pay for:
- Cyber extortion demands
- Costs of hiring experts to assist with negotiations
- Data breach notification costs
- Investigation into a cyber attack
This coverage can also pay for business interruption expenses, including the profits your company lost while dealing with the attack.
Insureon’s licensed agents can help you compare cyber liability coverage options. With the right policy in place, you can handle the situation with expert guidance at your side.
There’s no question that small businesses are increasingly in the crosshairs of cyber criminals. But you can lower the odds of an attack and prevent any lasting damage to your business if the worst does happen.
By educating your employees, beefing up your IT security, and buying the right insurance protection, you can keep your small business safe from cyber threats.

Because state laws regulate the investigation and handling of data breaches, it's important to know the notification requirements for your business location. Learn more about the laws for data breach notification in your state.
Get cyber liability insurance quotes from trusted carriers with Insureon
Complete Insureon's easy online application today to get insurance quotes from top-rated U.S. carriers. You can also consult with an insurance agent on your business insurance needs. Once you find the right types of coverage for your small business, you can begin coverage and get your certificate of insurance in less than 24 hours.
Jen Matteis, Content and Production Editor
Jen is an expert on small business insurance, a talented writer, and meticulous editor. She’s written and edited hundreds of articles to help inform small business owners about their insurance options. Prior to joining Insureon in 2018, Jen served as a senior copywriter at a digital marketing agency, and as a writer and editor for newspapers on both coasts. In her spare time, she writes fiction.









