
Georgia workers' compensation insurance
Georgia law requires businesses with three or more employees to provide workers’ compensation insurance. This policy provides medical benefits for employees who suffer a workplace injury.
Who needs workers’ comp insurance in Georgia?
Georgia requires any business that regularly employs three or more people to have workers’ compensation insurance. “Regular” refers to any person who works for a business on a regular basis, even if it is part-time, regardless of an employee’s average weekly wage.
If a business is incorporated, corporate officers are considered employees. Georgia allows up to five officers to waive coverage on themselves. However, waiving coverage does not mean that they don’t count for the purpose of being a business that employs three or more people.
Businesses with fewer than three employees should still considering buying workers' compensation coverage. It's an affordable policy for small businesses since the workers' compensation rate depends on the number of employees.
Do you need workers’ compensation if you are self-employed?
Sole proprietors, independent contractors and partners are exempt from workers’ compensation requirements in Georgia. In fact, independent contractors are not eligible for it in most circumstances under Georgia law.
Sole proprietors and partners can still elect to purchase workers' comp, which could be a smart move. If you're injured on the job, personal health insurance might deny the claim since it's related to your work. That would leave you paying for expensive medical bills, without any of the wage replacement support that workers' comp also provides.

Is workers’ compensation mandatory in Georgia for part-time employees?
Georgia law requires that regular part-time employees are covered by workers’ comp. This would include someone who only works on weekends, for example, as long as the employee works for the business on a regular basis.
Georgia requires any business that regularly employs three or more people to have workers’ compensation insurance.
What does workers' comp cover for Georgia businesses?
Here are several examples of how workers' compensation insurance coverage helps pay expenses for injured workers:
- A hairstylist burns their hand on a curling iron while styling a client's hair. Workers' comp covers their doctor's appointment and pain medication, as well as provides disability benefits to replace part of the wages they miss while they're recovering.
- A cleaning company employee suffers from respiratory problems after years of using harsh cleaning chemicals. After filing a workers' comp claim, they receive permanent disability payments for their ongoing lung issues.
- A retail store employee slips on a wet floor and hits their head. In this instance, workers' compensation would cover them during their emergency room trip, MRI, and any following medical expenses during their recovery.
- A nurse trips on a cord in their patient's room and breaks their wrist. Workers' comp covers the cost of the emergency room visit, surgery, medications, and then two months of physical therapy to help them recover.
What does workers' compensation insurance not cover?
Additionally, here's what your workers' comp policy won't cover:
- Injuries caused by intoxication, drugs, or company policy violations
- Injuries claimed after a firing or layoff
- Wages for a replacement worker
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) fines
How much does workers' compensation insurance cost in Georgia?

The average cost of workers’ compensation in Georgia is $49 per month.
Your workers' comp premium is calculated based on a few factors, including:
- Payroll
- Location, such as Atlanta, Macon, or Savannah
- Number of employees
- Industry and risk factors
- Coverage limits
- Claims history
How do you buy workers' compensation insurance in Georgia?
There are a few ways for Georgia employers to purchase a workers' compensation insurance policy:
- You can buy a policy from a private insurance company. You could contact each workers' compensation insurance carrier independently to compare their products and rates, but that's where agents and brokers like Insureon come in. As the nation's leading digital insurance agency, Insureon partners with 40+ top-rated insurance carriers to deliver the right coverage for your business. Fill out an easy online application to get started.
- You can apply for self-insurance. Your business must meet certain criteria to qualify for self-insurance, as dictated by the Georgia State Board of Workers' Compensation (SBWC).
- You can buy insurance through an assigned risk plan. Georgia offers businesses the option to get workers' comp coverage with the NCCI's Workers' Compensation Insurance Plan (WCIP) program if unable to acquire insurance from a private company.
Verified workers' compensation insurance reviews
Insurance providers use a specific formula for calculating workers' comp premiums: Classification rate x Experience modification rate x (Annual payroll / $100).
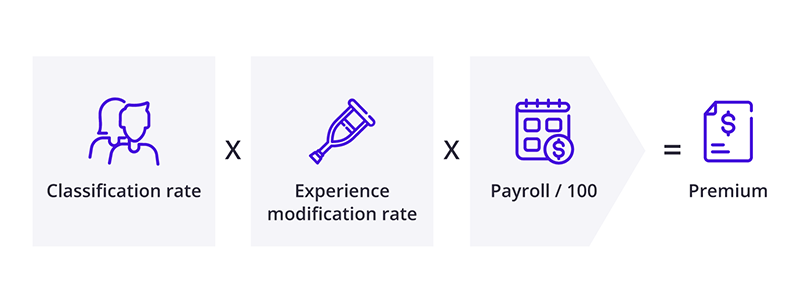
Here's a breakdown of this equation:
- The classification rate reflects your employees' risk. Each worker has a classification code for the type of work they do. Insurers look up those codes in a database to find the associated rate, which is lower for office workers and higher for carpenters, tree trimmers, and others with a higher rate of injuries. Like most other states, Georgia relies on the National Council on Compensation Insurance (NCCI) database.
- The experience modification rate (EMR) reflects your business's risk. The average experience modification rate is 1.0, which means a business is similar in risk to others in its profession. Higher EMRs reflect higher risks, such as a history of claims. The EMR only comes into play for annual workers' comp premiums of at least $5,000, so it's not a factor for many small business owners.
- The insurer multiplies these numbers with your payroll divided by 100 to come up with your workers' comp premium. Workers' compensation audits are typically done each year to ensure your business pays the right premium for this coverage.
How can Georgia business owners save money on workers' comp?
To save money on workers' comp insurance, it's important to make sure you classify your employees correctly. Employees with desk jobs or other jobs with a low risk of injury cost less to insure. This also helps you avoid misclassification fines.
In some cases, small business owners can choose to buy pay-as-you-go workers' compensation. This type of workers' comp policy has a low upfront premium, and lets you make payments based on your actual payroll instead of estimated payroll. It's useful for businesses that hire seasonal help or have fluctuating numbers of employees.
A ghost policy is a cheap option in some states, though it is not permitted in Georgia. A ghost policy is a workers' comp policy in name only. It provides no protection or medical benefits, but can fulfill contractual requirements for a workers' comp certificate at a reduced price.
Finally, a documented safety program can help lower workers' comp costs. A safer workplace means fewer accidents, which helps keep your premium low.
How does workers’ comp work in Georgia?
Under the Georgia workers' compensation law, coverage must begin for an employee on their first day of work.
When an employee suffers a work-related injury, workers' compensation insurance pays the cost of medical care provided by an authorized physician. That includes emergency treatment, hospitalization, prescriptions, and physical rehabilitation.
Workers' compensation also provides temporary partial disability benefits or temporary total disability benefits if the employee needs to take time off work. The amount is typically two-thirds of their average weekly wage.
In case of a catastrophic injury that leads to permanent partial disability or permanent total disability, such as loss of a body part, the injured employee receives weekly benefits for an amount of time determined by their injury.
In the event of a workplace fatality, workers' comp can help pay for funeral costs and death benefits for survivors.
Policies usually include employer's liability insurance, which can help cover legal expenses if an employee blames their employer for an injury. However, the exclusive remedy provision in most workers' comp policies prohibits an employee from suing their employer if they accept workers' comp benefits.
Explore the State Board of Workers' Compensation FAQs for details.
How do workers' comp claims work in Georgia?
Once an employer becomes aware that a job injury has occurred, they must immediately file a report with the insurer’s claims office. If the employee must be out of work for seven or more days, the employer must notify the Board of Workers’ Compensation within 21 days.
An employer can choose one of three methods for the insurance company to determine the amount of workers’ compensation benefits:
- Panel of physicians. This would consist of at least six non-associated physicians, including an orthopedist. No more than two physicians can be from industrial clinics, and the panel should include one physician who is a minority, where possible.
- Conformed panel of physicians. This panel requires a minimum of 10 physicians or professional associations. In addition to the same requirements as the panel of physicians option, this panel must include a general surgeon and chiropractor.
- Workers’ compensation managed care organization (MCO). This organization would be certified by the workers’ comp board to coordinate a plan that delivers and manages treatment under the Georgia Workers’ Compensation Act. This organization is also required to include minority providers.
What are the penalties for not having Georgia workers’ comp insurance?
If you fail to carry workers’ comp insurance in Georgia, there could be both civil and criminal penalties. The Georgia State Board of Workers’ Compensation regulates workers’ comp, and its enforcement division will investigate any incidents of noncompliance or allegations of fraud. In cases of noncompliance, employers could face:
- Liability: If an employer fails to provide the required workers’ comp coverage, the employer is responsible for compensating an employee for any injuries in the same manner as if there had been workers’ compensation insurance in place. The employer could be held responsible for attorney’s fees, civil penalties, and a 10% increase in compensation to the injured worker if the employer does not secure insurance.
- Civil penalties: Any person who violates workers’ comp regulations could face a penalty between $100 and $1,000 per violation. False statements made to the board could carry fines of $1,000 to $10,000 per violation. If an employer fails to provide the required insurance coverage, the civil penalty could be $500 to $5,000 per occurrence of a violation.
- Criminal penalties: An employer who refuses or willfully neglects to maintain insurance coverage could be found guilty of a misdemeanor. If convicted, the offense is punishable by a fine of $1,000 to $10,000, imprisonment up to one year, or both.
Workers’ compensation death benefits in Georgia
When a work accident leads to an employee's death, their beneficiaries are eligible to receive workers’ compensation death benefits. Georgia laws are designed to provide benefits to individuals who relied on the deceased worker for financial support. The spouse and children of a deceased employee are presumed to be dependents. There are a few conditions:
- A spouse must be legally married to the deceased. If the couple was living separately for 90 days prior to the date of injury or death, the claim could be denied if it is shown that the surviving spouse was not dependent. Common-law spouses might also be ineligible.
- Dependents include children under 18 years old, both biological and stepchildren, legally adopted children, and children born posthumously to the deceased. Children over 18 who are incapable of making a living because of a physical or mental disability and children under 22 years of age who are full-time students are also covered.
- Anyone else who can prove they were dependent on the deceased might be able to make a claim for benefits. (For example, an elderly parent.)
Workers’ compensation death benefits in Georgia include weekly payments to beneficiaries, burial expenses up to $7,500, and the deceased person’s medical bills.
Death benefits to a surviving spouse with no other dependents would be capped at $150,000 and are paid until age 65 or after 400 weeks of payments, based on whichever yields the larger amount. Benefits will end if the widowed spouse remarries or cohabitates with another person in a relationship.
Workers’ comp settlements in Georgia
Georgia’s State Board of Workers’ Compensation Settlement Division reviews and approves workers’ compensation settlements that include either lump sums or regular payments.
There are two forms of workers’ compensation settlements in Georgia:
Liability settlements resolve the claim, and the insurance company agrees to pay.
Non-liability settlements end a claim even where there is a dispute about benefit eligibility between stakeholders.
Regardless of whether there is a liability or non-liability settlement, once both parties (the employee and the insurance company) arrive at an agreement, the claim is closed. The employee cannot bring any additional claims for that injury.
Often, the board can approve a settlement based on the following documents:
- Stipulated settlement agreement, which explains the terms and conditions of your case
- Claim forms
- Medical records
- Information about unpaid child support
- Workers' compensation attorney's fee agreement and other fee documents
Lump sum settlements can either be a single payment or a structured settlement, which would mean that the payment is paid out monthly or annually for a specific period of time.
Statute of limitations for workers’ compensation claims
An injured worker is required to file a claim within the workers’ compensation statute of limitations. Georgia law has three separate provisions:
- All issues. Generally, the employee has one year from the date of injury to file a workers’ compensation claim.
- Change in condition. If the worker receives benefits for temporary, total, or partial disability, the injured person has two years from the date that the benefits ended to file a claim.
- Medical bill / mileage reimbursement. Once medical treatment has happened, the injured person has one year to submit the bill to their employer or workers’ compensation insurance company.
Get free workers' comp quotes with Insureon
If you are ready to buy a workers' compensation policy, start a free application with Insureon to compare quotes from top-rated insurance carriers. A licensed insurance agent will help answer your questions and explain your coverage options. Once you find the right policy, you can usually begin coverage and get your certificate of insurance in less than 24 hours.

Want free expert advice right in your inbox?
By entering your email address and subscribing, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy
