Workers' compensation insurance for technology businesses
Workers' compensation insurance covers medical costs and lost wages for work-related injuries and illnesses at your technology company. This policy is required in almost every state for businesses that have employees.
Workers' comp protects your tech employees
From IT consultants to software developers to PC builders, employees in every IT profession can suffer work-related accidents. Consequently, your tech business could be exposed to financial losses and litigation if you are held responsible.
Workers’ compensation insurance provides coverage in three primary areas:
- Employee work injury and illness medical expenses
- State law compliance
- Injured employee lawsuits
What coverage can workers' compensation insurance provide for IT businesses?
Employee work injury and illness expenses
If an employee suffers a work injury or develops an occupational illness, your business can be held responsible for their well-being. Workers’ compensation insurance helps cover:
- Medical bills, such as an emergency room visit
- Ongoing healthcare, such as physical rehabilitation and prescriptions
- Disability benefits while the injured worker is unable to work
- Death benefits for fatal incidents
Employee injury lawsuits
Employer’s liability insurance is typically included in a workers’ comp policy. It provides protection when an employee decides to sue a business owner over an injury.
Employer’s liability insurance can help cover:
- Attorney’s fees
- Court costs
- Settlements or judgments
Without insurance, you might have to pay for a costly legal battle – even if the suit is frivolous.
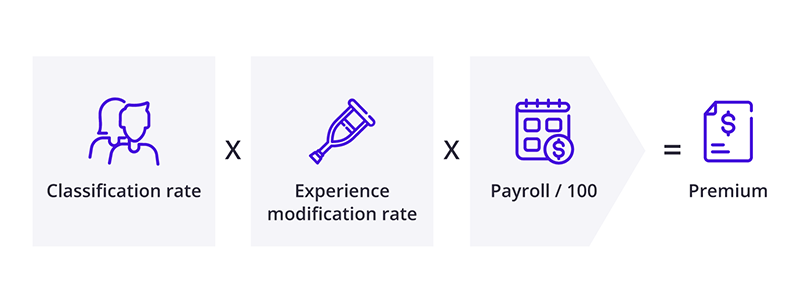
How are workers' comp insurance costs calculated for technology businesses?
The amount you pay for workers’ compensation is a specific rate based on every $100 of your business’s payroll. Insurance carriers determine your premium by the type of work done by your employees (classification rate), your experience modification rate (claims history), and your payroll (per $100).
The formula providers use in underwriting to calculate workers' comp rates is:
State laws set workers' comp requirements for technology companies
Each state has unique laws regarding workers’ compensation. For example, every technology business in New York must carry workers’ compensation insurance for its employees – even part-time workers. However, Alabama businesses are only required to carry workers’ compensation when they have five or more employees.
In most states, excluding Texas and South Dakota, tech companies are required to provide workers’ comp. Sole proprietors, independent contractors, and partners don’t have to carry workers’ compensation, but you can purchase a policy to protect yourself, too. It's a good idea, as health insurance providers can deny policyholder claims for injuries related to your work.
Workers' compensation laws in your state
Monopolistic state funds for workers' compensation coverage
In certain states, IT businesses must purchase coverage through a monopolistic workers' comp state fund. Those states are:
If you purchase workers’ comp through a monopolistic state fund, it might not include an employer’s liability insurance policy. However, you can purchase it as stop gap coverage from a private insurance company.

Lower workers' comp costs with risk management
Even if your employees are data analysts, web designers, or IT trainers who are in an office all day, they aren’t immune to harm. One of the most common work accidents is a slip or a fall that causes an injury. When an employee is injured at work, it can result in an insurance claim and a hike in your premium.
Business owners can manage their risks through workplace safety training and the reduction of workplace hazards. For example, you could:
- Tape down loose power cables
- Install brighter lights in a dim stairwell
- Provide ergonomic peripheral options for employees
- Proactively manage loss control
Taking these steps could reduce workplace injuries and help keep your insurance pricing low.
How much does workers' comp for technology businesses cost?

Technology businesses pay an average of $34 per month for a workers' compensation policy, but you could pay more or less depending on your risks.
Insurance costs for technology professionals are based on a few factors, including:
- IT services and technology products offered
- Business equipment and property
- Tech company size and revenue
- Insurance products purchased
- Policy limits and deductible
- Number of employees
- Workers' compensation claims history
Other important policies for IT businesses
Workers’ compensation insurance offers protection for your employees and to some extent your business, but it doesn’t provide coverage for all risks. Owners of small tech companies should also consider:
General liability insurance: This policy can cover expenses related to client injuries and property damage, along with advertising injuries like slander. Technology businesses, like data centers and SaaS companies, can often bundle it with commercial property insurance for savings in a business owner’s policy (BOP).
Errors and omissions insurance (E&O): This policy is critical for data scientists, managed service providers, and edtech professionals whose work depends on their expertise. Also called professional liability insurance, it can cover lawsuits related to a professional error, such as a mistake that causes a client’s server to crash.
Cyber insurance: You may want to invest in this coverage to protect your own company’s data, such as clients’ credit card numbers, or to protect against client lawsuits related to data breaches.
Fidelity bonds: IT companies, including cybersecurity and cloud computing businesses, are often privy to sensitive client data. This means an employee could jeopardize your business through unlawful access, theft, or fraud. Fidelity bonds safeguard your business against employees who engage in certain criminal acts.
Commercial auto insurance: This policy is required in most states for business-owned vehicles. It can cover property damage and medical bills in an accident involving your IT company vehicle, along with theft, vandalism, and weather damage.
Get free quotes and buy online with Insureon
Are you ready to safeguard your IT business with workers’ comp insurance? Complete Insureon’s easy online application today to compare quotes from leading U.S. carriers. Once you find a policy that fits your needs, you can obtain coverage in less than 24 hours.
Verified workers' compensation insurance reviews

Want free expert advice right in your inbox?
By entering your email address and subscribing, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy